题目
目的:Bone tissue engineering based on adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) is expected to become a new treatment for diabetic osteoporosis (DOP) patients with bone defects. However, compared with control ASCs (CON-ASCs), osteogenic potential of DOP-ASCs is decreased, which increased the difficulty of bone reconstruction in DOP patients. Moreover, the cause of the poor osteogenesis of ASCs in a hyperglycemic microenvironment has not been elucidated. Therefore, this study explored the molecular mechanism of the decline in the osteogenic potential of DOP-ASCs from the perspective of epigenetics to provide a possible therapeutic target for bone repair in DOP patients with bone defects.
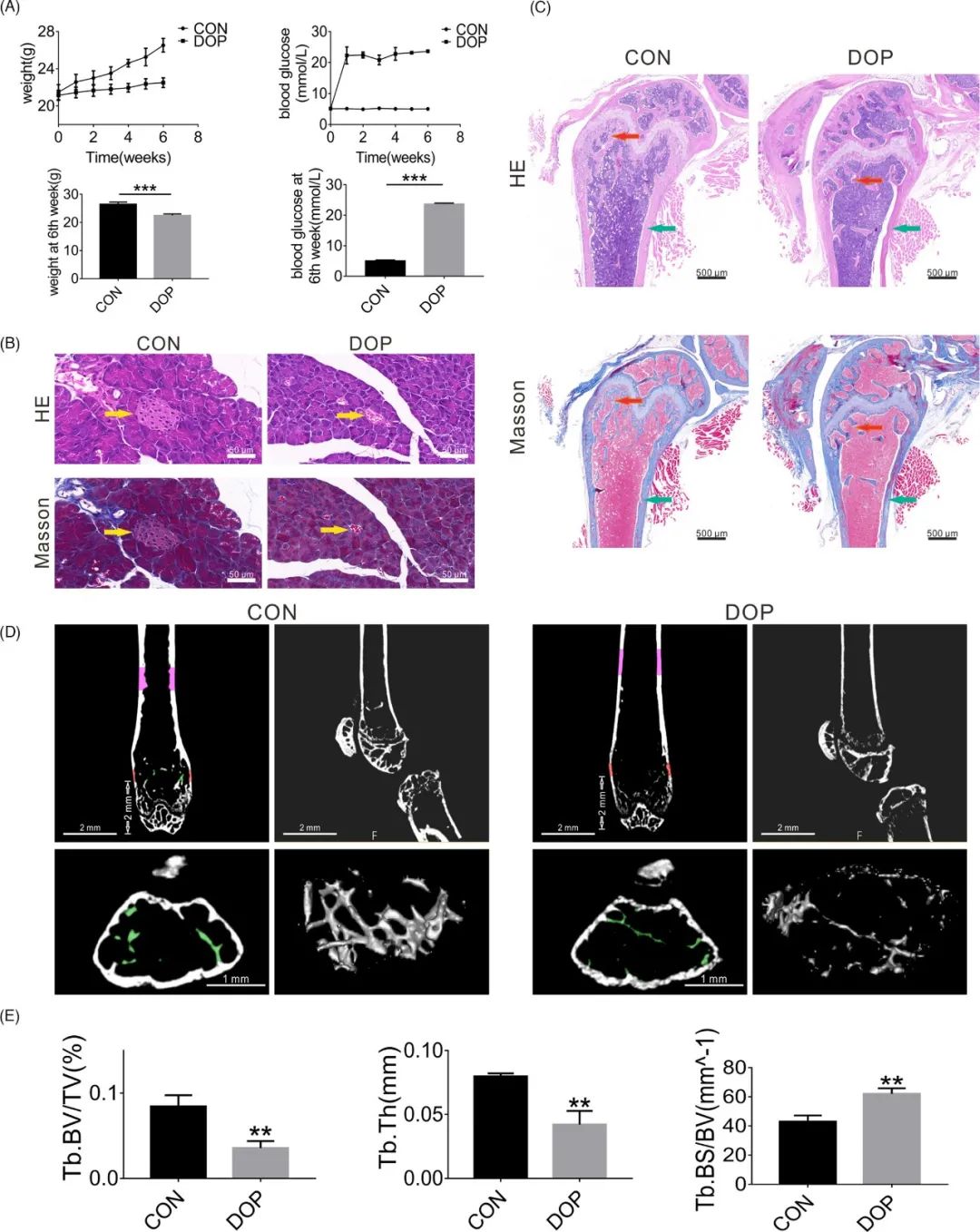
材料和方法:An animal model of DOP was established in mice. CON-ASCs and DOP-ASCs were isolated from CON and DOP mice, respectively. AK137033 small interfering RNA (SiRNA) and an AK137033 overexpression plasmid were used to regulate the expression of AK137033 in CON-ASCs and DOP-ASCs in vitro. Lentiviruses that carried shRNA-AK137033 or AK137033 cDNA were used to knockdown or overexpress AK137033, respectively, in CON-ASCs and DOP-ASCs in vivo. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Masson’s, alizarin red, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining, micro-computed tomography (Micro-CT), flow cytometry, qPCR, western blotting, immunofluorescence, and bisulfite-specific PCR (BSP) were used to analyze the functional changes of ASCs.
结果:The DOP mouse model was established successfully. Compared with CON-ASCs, AK137033 expression, the DNA methylation level of the sFrp2 promoter region, Wnt signaling pathway markers, and the osteogenic differentiation potential were decreased in DOP-ASCs. In vitro experiments showed that AK137033 silencing inhibited the Wnt signaling pathway and osteogenic ability of CON-ASCs by reducing the DNA methylation level in the sFrp2 promoter region. Additionally, overexpression of AK137033 in DOP-ASCs rescued these changes caused by DOP. Moreover, the same results were obtained in vivo.
结论:LncRNA-AK137033 inhibits the osteogenic potential of DOP-ASCs by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway via modulating the DNA methylation level in the sFrp2 promoter region. This study provides an important reference to find new targets for the treatment of bone defects in DOP patients.