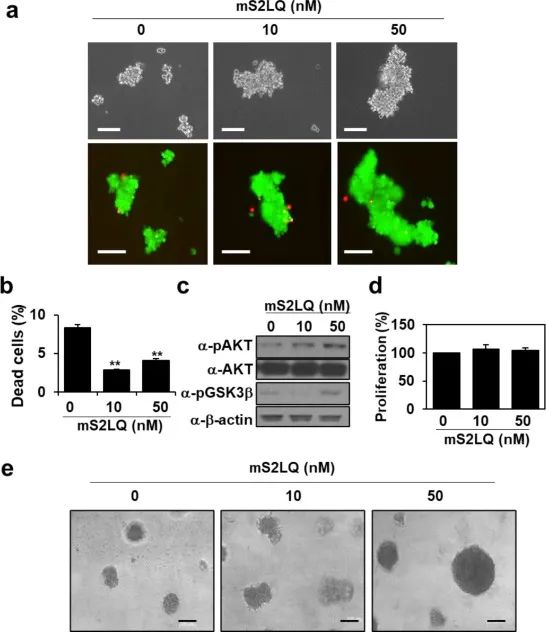
图2 syndecan-2肽可提高培养在悬浮液和3D基质中的CT26细胞存活率。a 活/死细胞染色鉴定,绿色=活细胞;红色=死细胞。b 流式细胞术检测细胞死亡率。c Western blot检测相关蛋白。d MTT检测细胞活性。e 3D培养7天后,相差显微镜观察细胞图像。
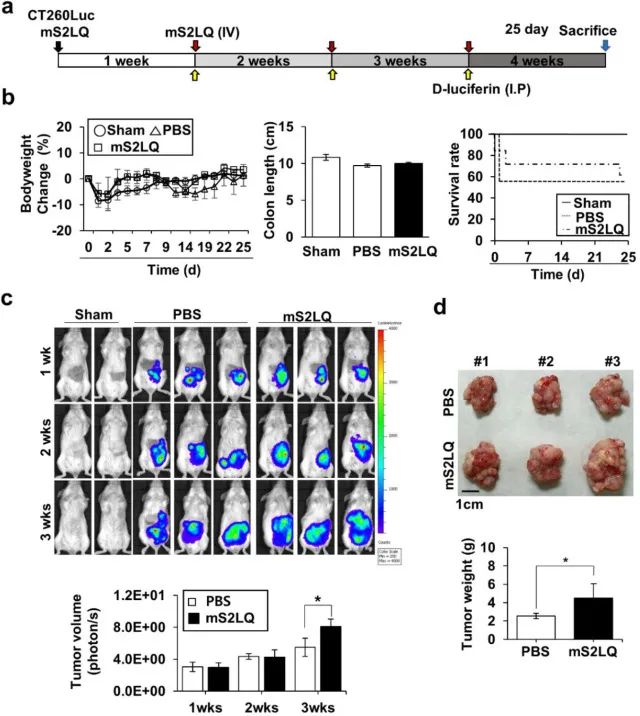
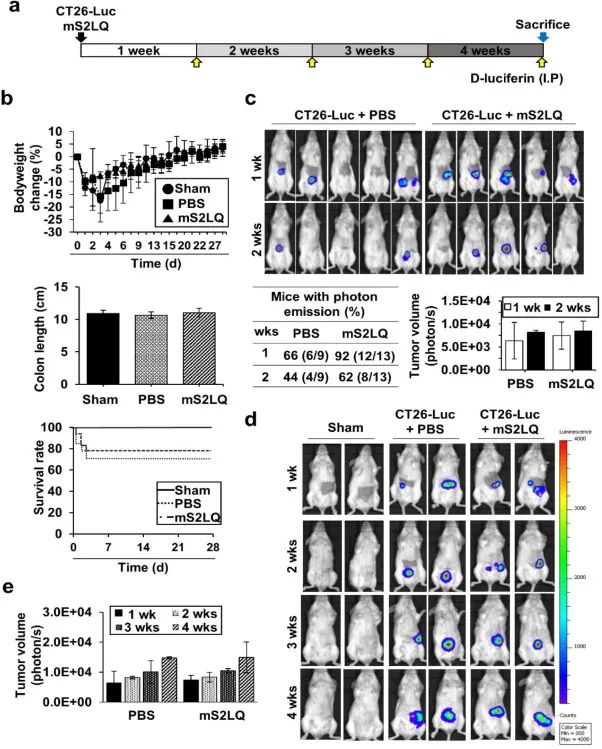
图3 尾静脉注射mS2LQ肽影响盲肠原位肿瘤的生长。a 实验时间表和重复静脉注射程序,箭头表示mS2LQ注射点。b 小鼠体重变化、结肠长度和存活率。c IVIS监测生物发光信号。d 结肠原位肿瘤离体图像(上图)与平均肿瘤重量(下图)。
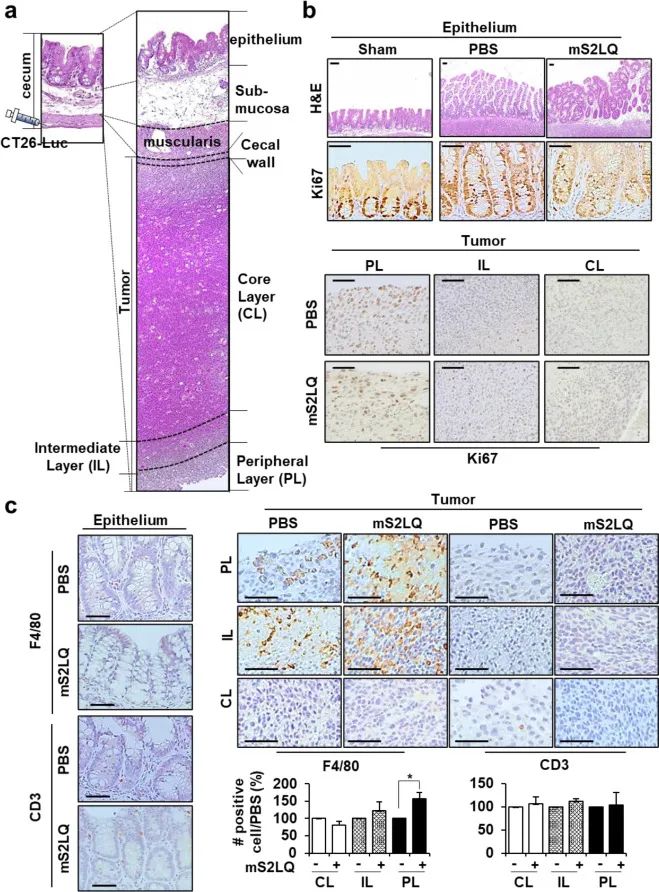
图4 血清S2LQ促进巨噬细胞对原位肿瘤组织周围区域的浸润。a 将CT26-Luc细胞实验性注射到盲肠壁以生成原位小鼠(左),注射后第25天原位肿瘤的组织图像(右),包括原位肿瘤(Tumor)和核心(CL)、中间(IL)和外周(PL)层。b HE染色与Ki67染色。c F4/80与CD3染色与阳性统计。
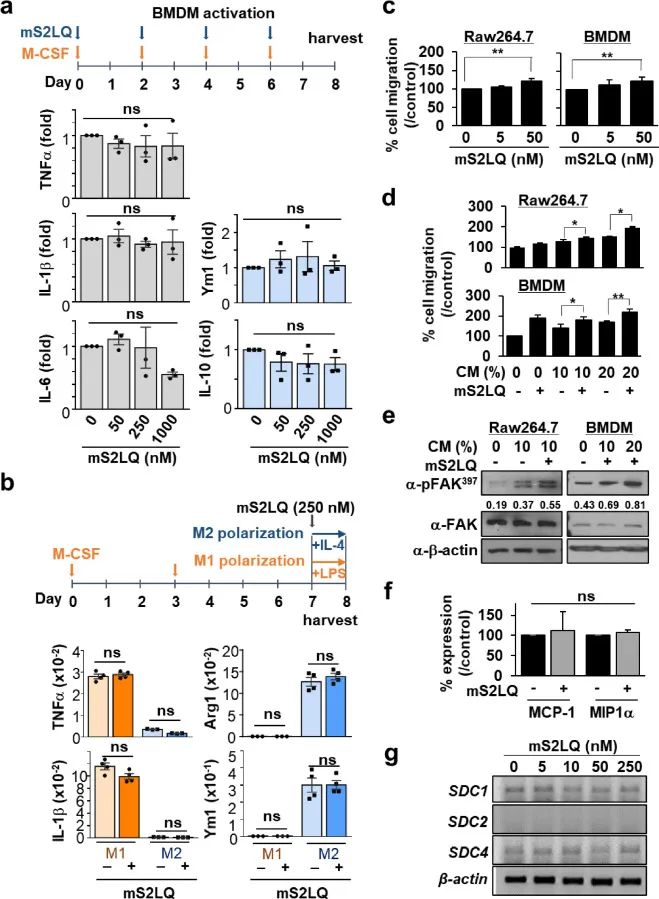
图5 S2LQ通过促进巨噬细胞迁移来增强巨噬细胞浸润。a 在有或没有mS2LQ情况下培养7天后,进行RT-PCR分析。b M-CSF处理7天后,在存在或不存在mS2LQ情况下经LPS或IL-4再刺激24h,RT-PCR检测M1和M2型标志物。c、d transwell实验检测RAW 264.7细胞与BMDM的迁移情况。e、g Western blot检测。f RT-PCR分析。

Shed syndecan-2 enhances colon cancer progression by increasing cooperative angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment
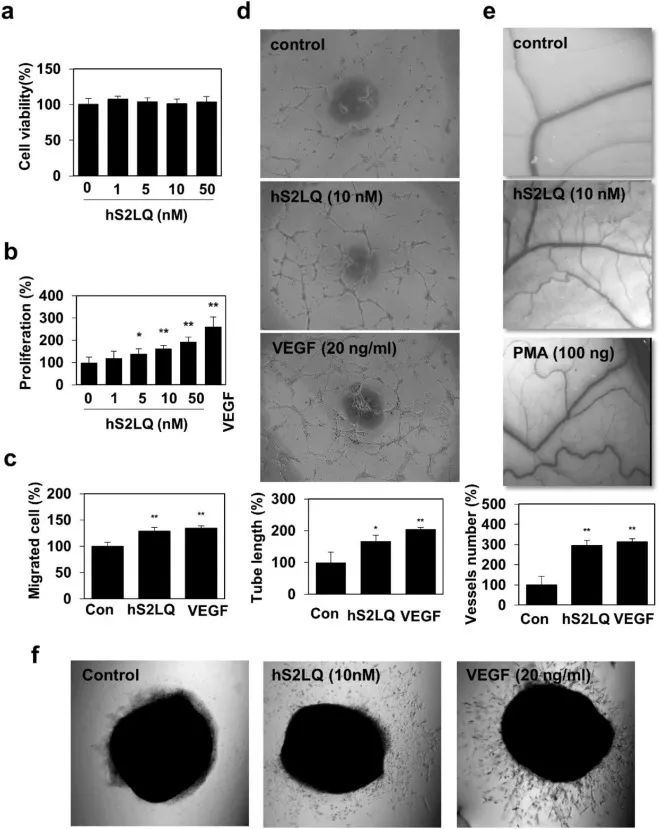
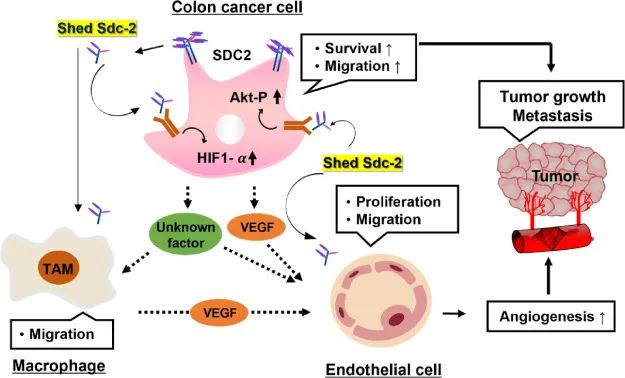
e show that shed syndecan-2 increases colon cancer progression by cooperatively promoting angiogenesis. Co-administration with a synthetic peptide of shed syndecan-2 (S2LQ) enhanced the survival and tumor engraftment of luciferase-expressing CT26 colon adenocarcinoma cells orthotopically implanted into the cecum of BALB/c mice. Intravenous injection of S2LQ further enhanced the growth of orthotopic tumors in the cecum, with increases in the tissue infiltration of macrophages and the formation of blood vessels, mainly in peripheral layers of the tumor facing the stroma. Furthermore, S2LQ stabilized HIF1α and enhanced the VEGF expression in human colon cancer cell lines, and increased the migration of RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells and bone marrow-derived macrophages. Finally, S2LQ increased the tube formation of vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Together, these data demonstrate that shed syndecan-2 enhances tumorigenic activity by increasing the crosstalk of cancer cells with tumor-associated macrophages and endothelial cells to enhance angiogenesis for colon cancer progression in the tumor microenvironment.
关键词:Syndecan-2;Angiogenesis;Orthotopic model;Tumor microenvironment