题目
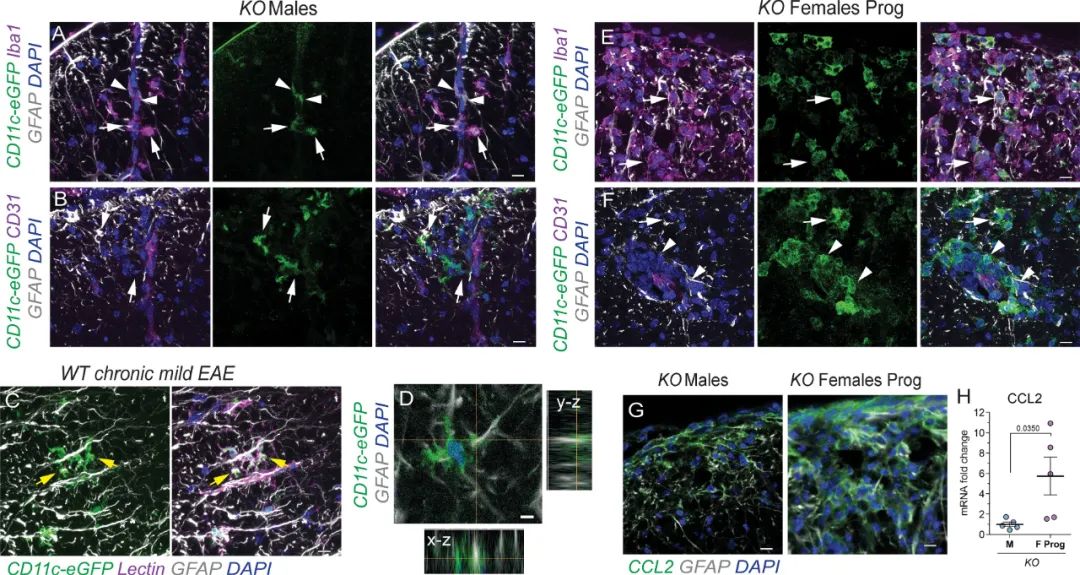
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune demyelinating disease with high variability of clinical symptoms. In most cases MS appears as a relapsing-remitting disease course that at a later stage transitions into irreversible progressive decline of neurologic function. The mechanisms underlying MS progression remain poorly understood. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an animal model of MS. Here we demonstrate that mice that develop mild EAE after immunization with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein 35–55 are prone to undergo clinical progression around 30days after EAE induction. EAE progression was associated with reduction in CD11c+ microglia and dispersed coalescent parenchymal infiltration. We found sex-dependent differences mediated by p38α signaling, a key regulator of inflammation. Selective reduction of CD11c+ microglia in female mice with CD11c-promoter driven p38α knockout (KO) correlated with increased rate of EAE progression. In protected animals, we found CD11c+ microglia forming contacts with astrocyte processes at the glia limitans and immune cells retained within perivascular spaces. Together, our study identified pathological hallmarks of chronic EAE progression and suggests that CD11c+ microglia may regulate immune cell parenchymal infiltration in autoimmune demyelination.
关键词:CD11c+ microglia;EAE progression;CNS infiltration;p38α sexual dimorphism;Glia limitans