doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02149-5.
CircRNA-DOPEY2 enhances the chemosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting CPEB4-mediated Mcl-1 translation
方法:Bioinformatics analysis was used to profile and identify the circRNAs involved in cisplatin responsiveness in ESCC. The chemosensitive role of cDOPEY2 was confirmed both in vitro and in vivo. The molecular mechanism of cDOPEY2 was investigated by mass spectrometry, immunoprecipitation, and ubiquitination analyses.
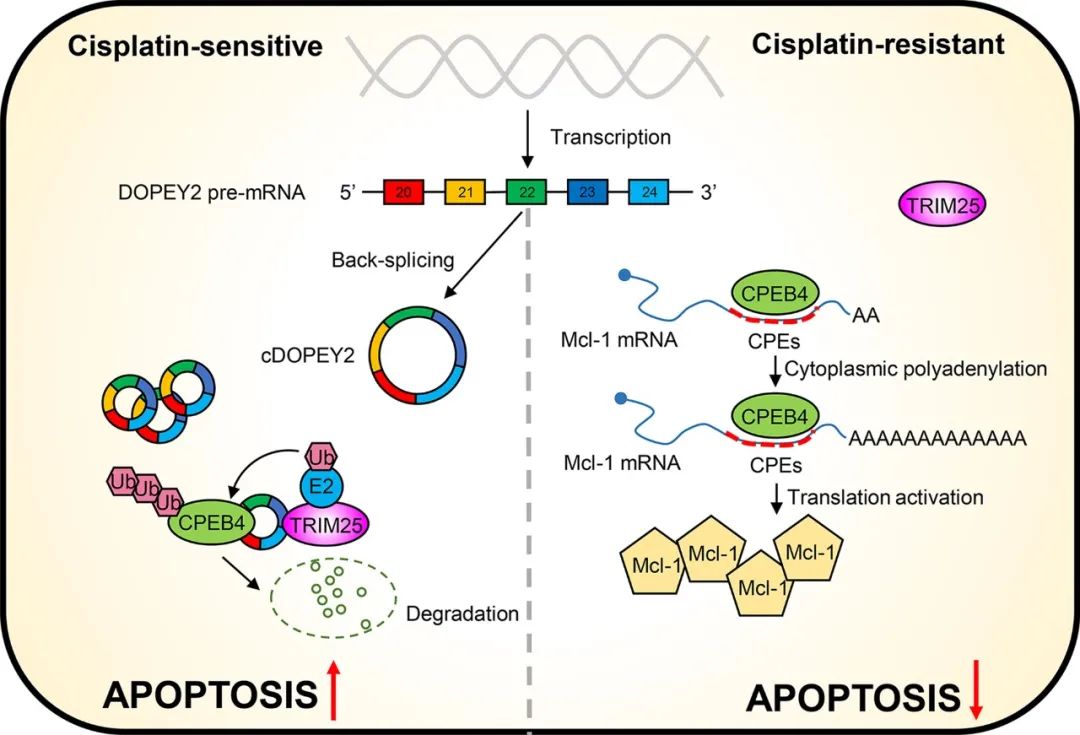
结果:We report that a novel circRNA (cDOPYE2, hsa_circ_0008078) was markedly downregulated in cisplatin-resistant ESCC cells (ESCC-CR) compared with parental chemosensitive cells. Re-expression of cDOPEY2 substan-tially enhanced the cell-killing ability of cisplatin by augmenting the apoptotic process in ESCC-CR cells, which was achieved by decreasing the abundance of the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1. Mechanistically, we showed that cDOPEY2 acted as a protein scaffold to enhance the interaction between the cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein (CPEB4) and the E3 ligase TRIM25, which in turn facilitated the ubiquitination and degradation of CPEB4. The increased Mcl-1 expression in ESCC-CR cells was dependent on the binding of CPEB4 to its untranslated mRNA, and depletion of CPEB4 mediated by cDOPEY2 reversed this effect. Rescue experiments confirmed that the critical role of cDOPEY2 in maintaining cisplatin sensitivity was dependent on the depletion of CEPB4 and its downstream target Mcl-1. Clinical and in vivo data further corroborated the significant relevance of cDOPEY2 to cisplatin responsiveness in ESCC.
结论:We provide evidence that cDOPEY2 inhibits CPEB4-mediated Mcl-1 translation by promoting the ubiq-uitination and degradation of CPEB4 to alleviate cisplatin resistance, indicating that cDOPEY2 may serve as a valuable biomarker and potential therapeutic target in ESCC.
关键词:Circular RNA, Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, Cisplatin resistance, CPEB4, Mcl-1