doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.10.011.
NFIL3 deficiency alleviates EAE through regulating different immune cell subsets
背景:The transcription factor NFIL3 exerts comprehensive effects on the immune system. Previous studies revealed that NFIL3 is related to the function and development of different immune cell subsets. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is mediated by immune cells which results in inflammatory demyelination in the central nervous system (CNS). However, how NFIL3 affects EAE has not been thoroughly studied.
目标:The current study aimed to investigate how NFIL3 affects EAE, especially the changes of T cells and dendritic cells as well as the crosstalk between them.
方法:We used NFIL3-/- mice and C57BL/6J mice (wildtype) to establish MOG35-55-induced EAE. The clinical scores were recorded daily. The immune cells within and outside the CNS of EAE mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. Histology was used to evaluated the neuroinflammation and demyelination in the CNS. Besides, CD11c+ dendritic cells (DCs) were cocultured with T cells and the interplay was measured.
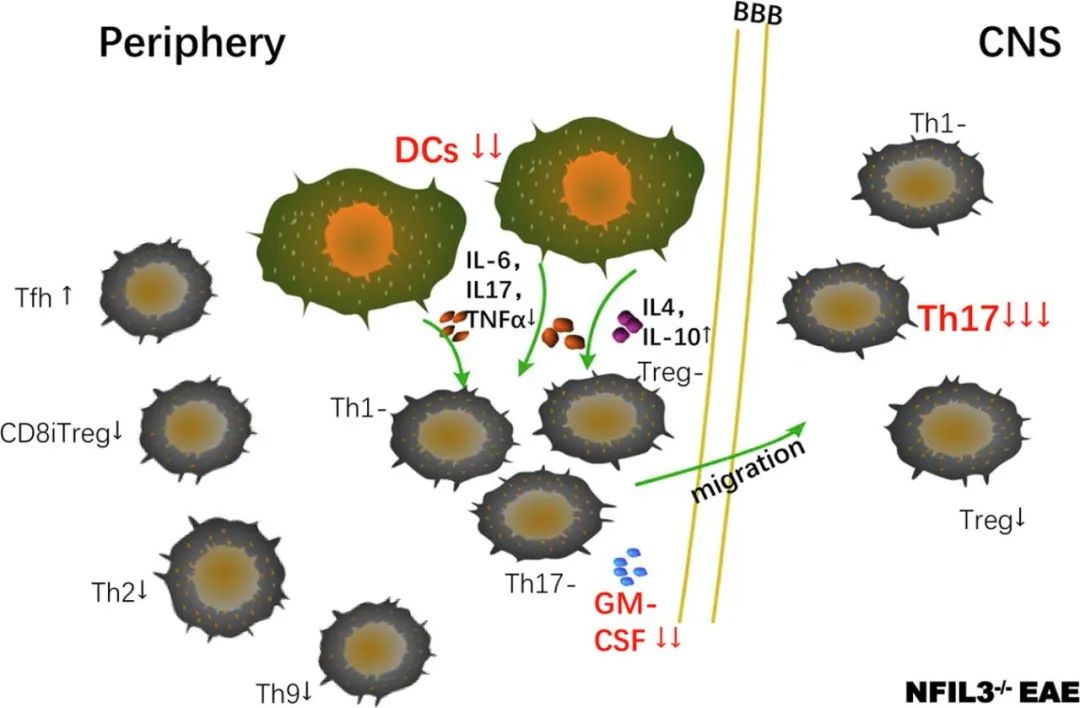
结果:At the peak of EAE, Th17 cells decreased within the CNS accompanying with lower clinical scores and milder neuroinflammation and demyelination in NFIL3 knockout EAE mice. Outside the CNS, PD-1 and ICOS on CD4+T cells increased, whereas Th2, Th9, CD8+CD103+T cells and GM-CSF+CD4+T cells decreased. Besides, the pro-inflammatory capacity of NFIL3-/-CD11c+ dendritic cells was impaired while the anti-inflammatory capacity was promoted.
结论:This study suggests that NFIL3 deficiency could alleviate MOG35-55-induced EAE through regulating different immune cell subsets, which is not only related with adaptive immunity and innate immunity, but also related with the cross-talk between them, especially CD4+T cells and CD11c+ dendritic cells.