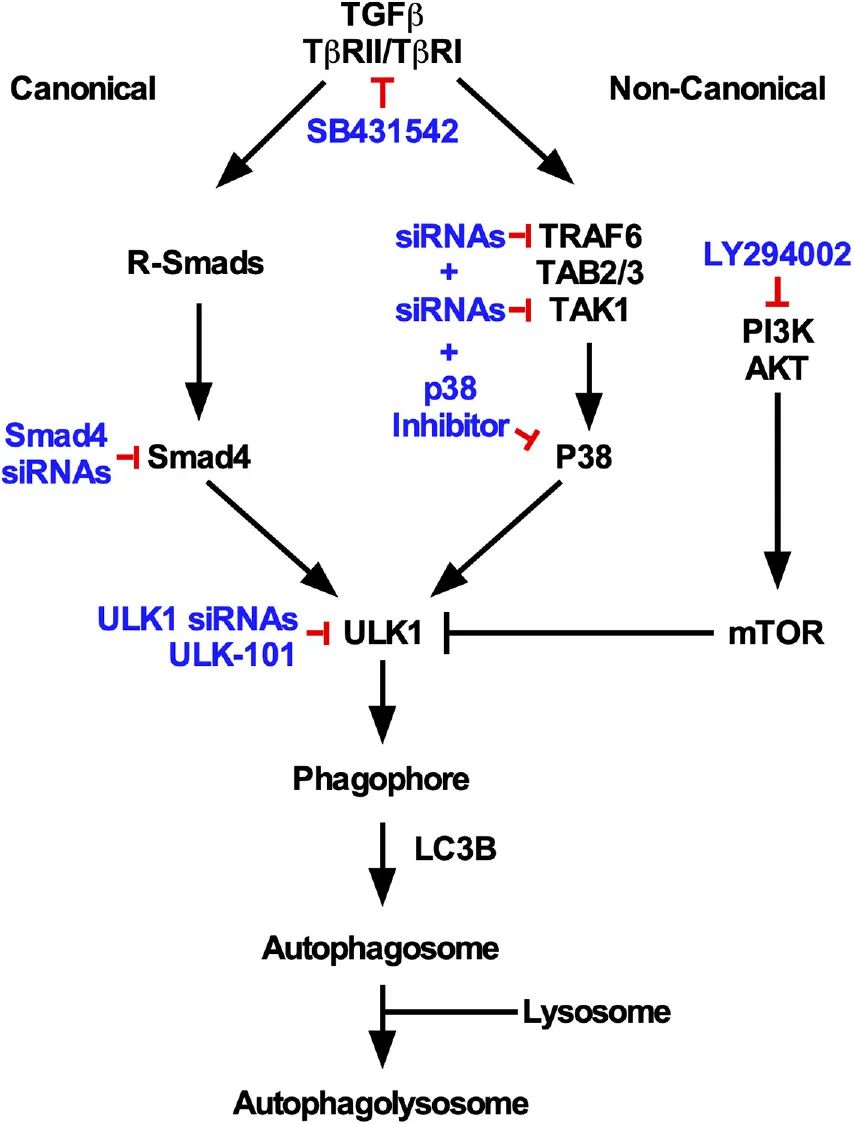
图 NSCLC细胞中TGFβ1依赖性自噬总结的模式图。特定的经典和非经典TGFβ依赖性自噬的关键都集中在ULK1活性上,并且ULK1也是溶酶体靶向LC3B所必需的。
期刊及DOI号
Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 25.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.712124.
题目
Canonical and Non-canonical TGFβ Signaling Activate Autophagy in an ULK1-Dependent Manner
The mechanism(s) in which transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ) modulates autophagy in cancer remain unclear. Here, we characterized the TGFβ signaling pathways that induce autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells, using cells lines stably expressing GFP-LC3-RFP-LC3ΔG constructs that measure autophagic flux. We demonstrated that TGFβ1 increases Unc 51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) protein levels, 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent ULK1 phosphorylation at serine (S) 555 and ULK1 complex formation but decreases mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity on ULK1. Further analysis revealed that the canonical Smad4 pathway and the non-canonical TGFβ activated kinase 1/tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6/P38 mitogen activated protein kinase (TAK1-TRAF6-P38 MAPK) pathway are important for TGFβ1-induced autophagy. The TAK1-TRAF6-P38 MAPK pathway was essential for downregulating mTOR S2448 phosphorylation, ULK1 S555 phosphorylation and autophagosome formation. Furthermore, although siRNA-mediated Smad4 silencing did not alter mTOR-dependent ULK1 S757 phosphorylation, it did reduce AMPK-dependent ULK1 S555 phosphorylation and autophagosome formation. Additionally, Smad4 silencing and inhibiting the TAK1-TRAF6-P38 MAPK pathway decreased autophagosome-lysosome co-localization in the presence of TGFβ. Our results suggest that the Smad4 and TAK1-TRAF6-P38 MAPK signaling pathways are essential for TGFβ-induced autophagy and provide specific targets for the inhibition of TGFβ in tumor cells that utilize autophagy in their epithelial-mesenchymal transition program.