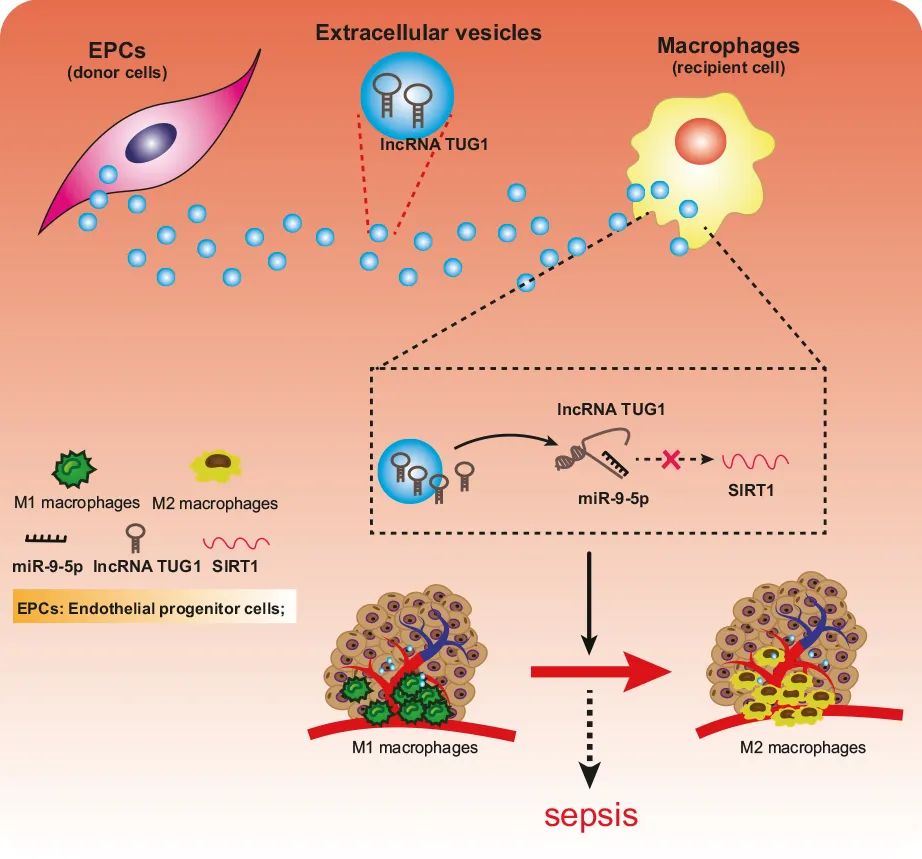
图 TUG1/miR-9-5p/SIRT1信号通路在败血症巨噬细胞极化调节中的功能作用示意图。TUG1在脓毒症中下调,其可削弱miR-9-5p对SIRT1的靶向抑制,有助于改善败血症引起的炎症损伤。
Cell Death Dis. 2021 Nov 6.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04117-5.
题目
Functional delivery of lncRNA TUG1 by endothelial progenitor cells derived extracellular vesicles confers anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization in sepsis via impairing miR-9-5p-targeted SIRT1 inhibition
The delivery of biomolecules by extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) has been proven to ameliorate sepsis, yet the therapeutic mechanism remains to be elucidated. Taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) is a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) that is downregulated in sepsis. The current study was designed to explore the role of EPCs derived EVs transmitting TUG1 in macrophage polarization and macrophage-mediated inflammation in a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis mouse model. TUG1 was underexpressed in CLP-induced sepsis, and its reexpression induced anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization and suppressed macrophage-medicated inflammatory injury to the pulmonary vascular endothelium. EPCs derived EVs transmitted TUG1 to promote M2 macrophage polarization. Luciferase, RIP, and RNA pull-down assays showed that TUG1 could competitively bind to microRNA-9-5p (miR-9-5p) to upregulate the expression of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). Furthermore, EPCs derived EVs transmitted TUG1 to promote M2 macrophage polarization through the impairment of miR-9-5p-dependent SIRT1 inhibition. Finally, EPCs derived EVs carrying TUG1 were verified to ameliorate sepsis-induced organ damage in the murine model. In summary, EPCs derived EVs transmit TUG1 to attenuate sepsis via macrophage M2 polarization. This study also highlights the proinflammatory mechanism associated with miR-9-5p-mediated inhibition of SIRT1, which contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of sepsis.