J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 14.
doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02207-y.
题目
Blockade of glutamine-dependent cell survival augments antitumor efficacy of CPI-613 in head and neck cancer
背景:Alterations in metabolism are one of the emerging hallmarks of cancer cells and targeting dysregulated cancer metabolism provides a new approach to developing more selective therapeutics. However, insufficient blockade critical metabolic dependencies of cancer allows the development of metabolic bypasses, thus limiting therapeutic benefits.
方法:A series of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell lines and animal models were used to determine the efficacy of CPI-613 and CB-839 when given alone or in combination. Glutaminase 1 (GLS1) depletion was achieved by lentiviral shRNAs. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined in HNSCC cells cultured in 2D culture dish and SeedEZ™ 3D scaffold. Molecular alterations were examined by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Metabolic changes were assessed by glucose uptake, lactate production, glutathione levels, and oxygen consumption rate.
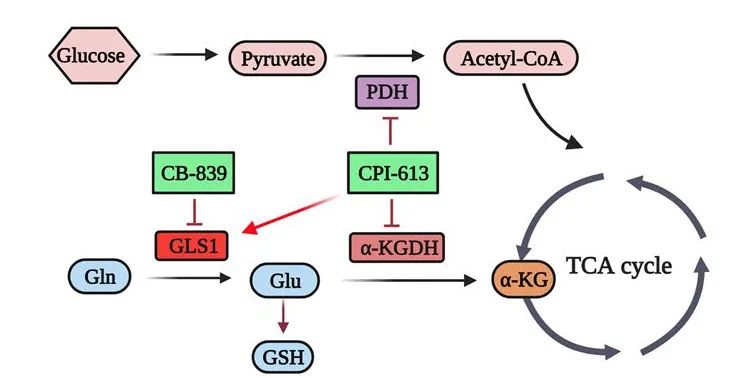
结果:We show here that HNSCC cells display strong addiction to glutamine. CPI-613, a novel lipoate analog, redirects cellular activity towards tumor-promoting glutaminolysis, leading to low anticancer efficacy in HNSCC cells. Mechanistically, CPI-613 inhibits the tricarboxylic acid cycle by blocking the enzyme activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, which upregulates GLS1 and eventually promotes the compensatory role of glutaminolysis in cancer cell survival. Most importantly, the addition of a GLS1 inhibitor CB-839 to CPI-613 treatment abrogates the metabolic dependency of HNSCC cells on glutamine, achieving a synergistic anticancer effect in glutamine-addicted HNSCC.
结论:These findings uncover the critical role of GLS1-mediated glutaminolysis in CPI-613 treatment and suggest that the CB-839 and CPI-613 combination may potentiate synergistic anticancer activity for HNSCC therapeutic gain.