J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jan 7.
doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02224-x.
题目
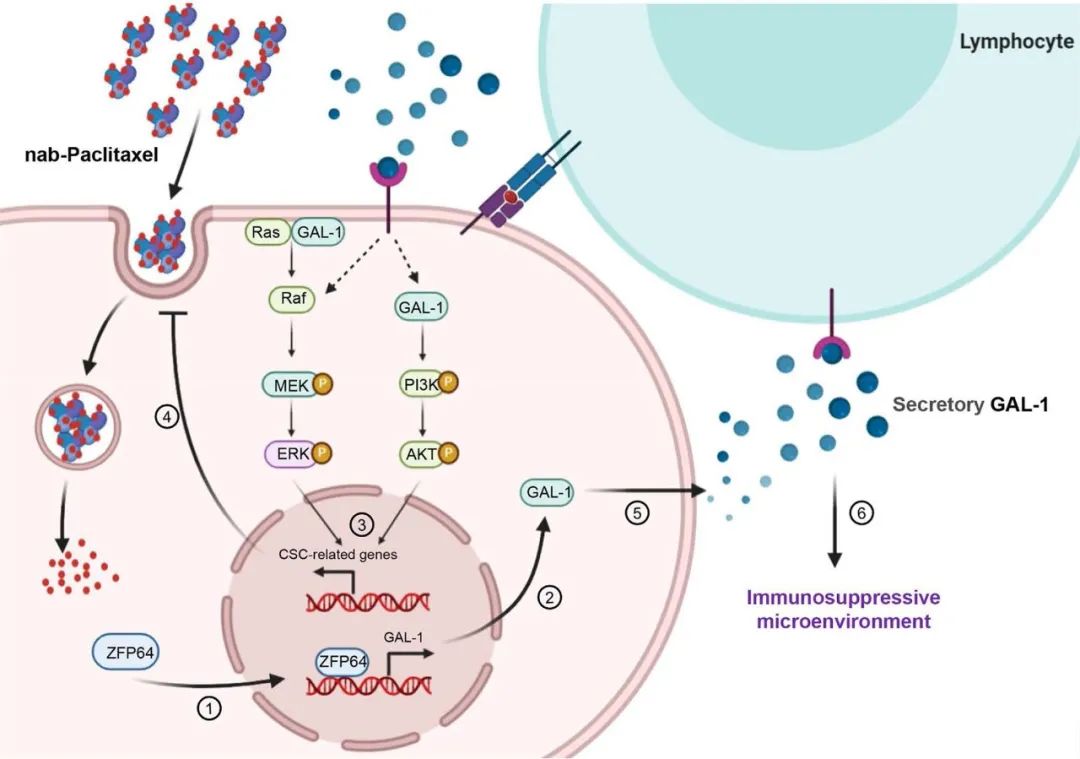
Targeting ZFP64/GAL-1 axis promotes therapeutic effect of nab-paclitaxel and reverses immunosuppressive microenvironment in gastric cancer
背景:Chemoresistance is a main obstacle in gastric cancer (GC) treatment, but its molecular mechanism still needs to be elucidated. Here, we aim to reveal the underlying mechanisms of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel) resistance in GC.
方法:We performed RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) on samples from patients who were resistant or sensitive to nab-paclitaxel, and identified Zinc Finger Protein 64 (ZFP64) as critical for nab-paclitaxel resistance in GC. CCK8, flow cytometry, TUNEL staining, sphere formation assays were performed to investigate the effects of ZFP64 in vitro, while subcutaneous tumor formation models were established in nude mice or humanized mice to evaluate the biological roles of ZFP64 in vivo. Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (CHIP-seq) and double-luciferase reporter gene assay were conducted to reveal the underlying mechanism of ZFP64.
结果:ZFP64 overexpression was linked with aggressive phenotypes, nab-paclitaxel resistance and served as an independent prognostic factor in GC. As a transcription factor, ZFP64 directly binds to Galectin-1 (GAL-1) promoter and promoted GAL-1 transcription, thus inducing stem-cell like phenotypes and immunosuppressive microenviron-ment in GC. Importantly, compared to treatment with nab-paclitaxel alone, nab-paclitaxel plus GAL-1 blockade signifi-cantly enhanced the anti-tumor effect in mouse models, particularly in humanized mice.
结论:Our data support a pivotal role for ZFP64 in GC progression by simultaneously promoting cellular chemotherapy resistance and tumor immunosuppression. Treatment with the combination of nab-paclitaxel and a GAL-1 inhibitor might benefit a subgroup of GC patients.
关键词:Gastric cancer, Chemoresistance, ZFP64, Cancer stem cell, Immunosuppression