泛素化是由E1、E2、E3泛素连接酶控制的三步酶促反应,在这些酶中,E3泛素连接酶是反应特异性的关键,已知包括ITCH在内的HECT型E3泛素连接酶可通过泛素化各种底物来多方面调节细胞功能,这些连接酶是变构自抑制的,需要激活蛋白才能完全实现其底物的泛素化。2021年12月20日,日本长手爱知医科大学医学院病理学系Kenji Kasai团队在EMBO reports上发表了题为“ENTREP/FAM189A2 encodes a new ITCH ubiquitin ligase activator that is downregulated in breast cancer”的研究论文。在本研究中,团队证明FAM189A2在乳腺癌中下调,可编码一种新型ITCH激活剂,其本质上是一种含有PPxY基序的跨膜蛋白,这些基序介导了其与ITCH的关联和泛素化,介于FAM189A2是ITCH使CXCR4活性脱敏的独特激活剂,团队也建议将FAM189A2重命名为ENTREP。
研究发现,E3泛素连接酶可识别E2泛素连接酶结合的泛素和特定底物,并将泛素转移到赖氨酸残基或底物的氨基末端,其家族成员依据结构相似性和泛素化域分为四种主要类型:HECT型、RING型、RBR型以及包含U-box结构域的E3连接酶,其中,HECT型E3泛素连接酶因其在维持细胞稳态中的关键作用而备受关注。据报道,在配体刺激下,细胞会通过细胞表面受体转导细胞内信号以诱导细胞反应,然而,过度刺激会导致细胞毒性或细胞功能受损,易患癌症和其他疾病。内吞作用始于配体诱导的受体翻译后修饰,包括磷酸化和泛素化,泛素化受体可被CLASP识别,特别是,HECT型E3连接酶的NEDD4亚族(包括ITCH和NEDD4L),可表现出C2域介导的质膜积累并参与受体泛素化和内吞作用。其中ITCH泛素化与增强趋化因子受体CXCR4内吞作用后,其下游信号可促进癌细胞迁移和干细胞样特性。
研究团队之前已将FAM189A2/C9orf61/X123鉴定为乳腺癌中的下调基因,但其功能仍然未知,在本研究中,团队继续探索了FAM189A2基因功能,发现,FAM189A2在质膜上与ITCH结合,不仅以PPxY基序依赖性方式接受ITCH介导的泛素化,也可与Epsin结合并与ITCH一起在早期和晚期核内体中积累,表明FAM189A2参与了网格蛋白介导的内吞作用。有趣的是,FAM189A2促进了趋化因子受体CXCR4与ITCH的结合,并增强了ITCH介导的CXCR4泛素化。FAM189A2敲除抑制CXCL12诱导的CXCR4内吞作用,从而增强CXCL12对乳腺癌细胞趋化性和乳腺球形成的影响。
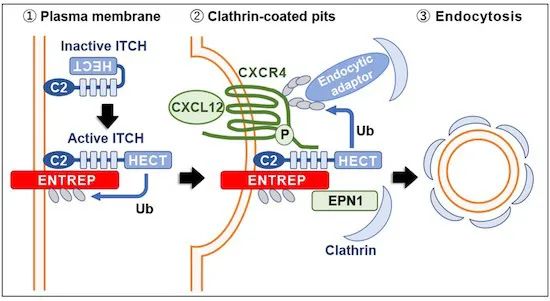
图 本文图形摘要示意图。ENTREP是HECT型E3泛素连接酶ITCH的激活剂,可介导趋化因子受体CXCR4的泛素化和内吞作用;ENTREP下调减弱了CXCR4的脱敏性,从而促进了乳腺癌干性。
EMBO Rep. 2021 Dec 20.
doi: 10.15252/embr.202051182.
题目
ENTREP/FAM189A2 encodes a new ITCH ubiquitin ligase activator that is downregulated in breast cancer
The HECT-type ubiquitin E3 ligases including ITCH regulate many aspects of cellular function through ubiquitinating various substrates. These ligases are known to be allosterically autoinhibited and to require an activator protein to fully achieve the ubiquitination of their substrates. Here we demonstrate that FAM189A2, a downregulated gene in breast cancer, encodes a new type of ITCH activator. FAM189A2 is a transmembrane protein harboring PPxY motifs, and the motifs mediate its association with and ubiquitination by ITCH. FAM189A2 also associates with Epsin and accumulates in early and late endosomes along with ITCH. Intriguingly, FAM189A2 facilitates the association of a chemokine receptor CXCR4 with ITCH and enhances ITCH-mediated ubiquitination of CXCR4. FAM189A2-knockout prohibits CXCL12-induced endocytosis of CXCR4, thereby enhancing the effects of CXCL12 on the chemotaxis and mammosphere formation of breast cancer cells. In comparison to other activators or adaptors known in the previous studies, FAM189A2 is a unique activator for ITCH to desensitize CXCR4 activity, and we here propose that FAM189A2 be renamed as ENdosomal TRansmembrane binding with EPsin (ENTREP).